Prerequisites
Before you begin make sure you have the following requirements in place:
- An Azure account with an active subscription. If you don’t already have one, you can sign up for a free trial at https://azure.com/free.
- The Azure Functions Core Tools version 4.x.
- Visual Studio Code on one of the supported platforms.
- .NET 6 is the target framework for the steps below.
- The C# extension for Visual Studio Code.
- The Azure Functions extension for Visual Studio Code.
Create your local project
In this section, you use Visual Studio Code to create a local Azure Functions project in C#. Later in this exercise, you’ll publish your function code to Azure.
- Choose the Azure icon in the Activity bar, then in the Workspace area, select Add…. Finally, select Create Function….
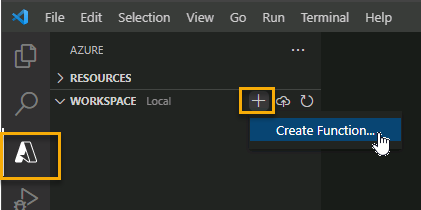 NoteA pop-up message will likely appear prompting you to create a new project, if it does select Create new project.
NoteA pop-up message will likely appear prompting you to create a new project, if it does select Create new project. - Choose a directory location for your project workspace and choose Select. NoteBe sure to select a project folder that is outside of an existing workspace.
- Provide the following information at the prompts:
- Select a language: Choose
C#. - Select a .NET runtime: Choose
.NET 6 - Select a template for your project’s first function: Choose
HTTP trigger. - Provide a function name: Type
HttpExample. - Provide a namespace: Type
My.Function. - Authorization level: Choose
Anonymous, which enables anyone to call your function endpoint. - Select how you would like to open your project: Choose
Add to workspace.
- Select a language: Choose
Using this information, Visual Studio Code generates an Azure Functions project with an HTTP trigger.
Run the function locally
Visual Studio Code integrates with Azure Functions Core tools to let you run this project on your local development computer before you publish to Azure.
- Make sure the terminal is open in Visual Studio Code. You can open the terminal by selecting Terminal and then New Terminal in the menu bar.
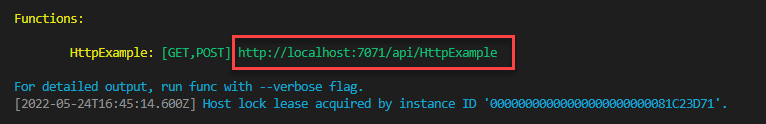
- Press F5 to start the function app project in the debugger. Output from Core Tools is displayed in the Terminal panel. Your app starts in the Terminal panel. You can see the URL endpoint of your HTTP-triggered function running locally.
- With Core Tools running, go to the Azure: Functions area. Under Functions, expand Local Project > Functions. Right-click the
HttpExamplefunction and choose Execute Function Now….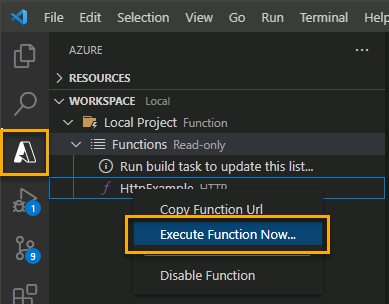
- In Enter request body type the request message body value of
{ "name": "Azure" }. Press Enter to send this request message to your function. When the function executes locally and returns a response, a notification is raised in Visual Studio Code. Information about the function execution is shown in Terminal panel. - Press Shift + F5 to stop Core Tools and disconnect the debugger.
After you’ve verified that the function runs correctly on your local computer, it’s time to use Visual Studio Code to publish the project directly to Azure.
Sign in to Azure
Before you can publish your app, you must sign in to Azure. If you’re already signed in, go to the next section.
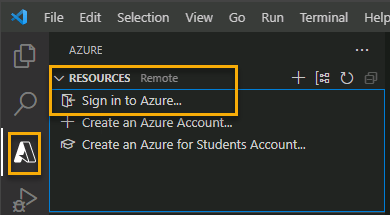
- If you aren’t already signed in, choose the Azure icon in the Activity bar, then in the Azure: Functions area, choose Sign in to Azure….
- When prompted in the browser, choose your Azure account and sign in using your Azure account credentials.
- After you’ve successfully signed in, you can close the new browser window. The subscriptions that belong to your Azure account are displayed in the Side bar.
Create resources in Azure
In this section, you create the Azure resources you need to deploy your local function app.
- Choose the Azure icon in the Activity bar, then in the Resources area select the Create resource… button.
- Provide the following information at the prompts:
- Select Create Function App in Azure…
- Enter a globally unique name for the function app: Type a name that is valid in a URL path. The name you type is validated to make sure that it’s unique in Azure Functions.
- Select a runtime stack: Use the same choice you made in the Create your local project section above.
- Select a location for new resources: For better performance, choose a region near you.
- Select subscription: Choose the subscription to use. You won’t see this if you only have one subscription.
- When completed, the following Azure resources are created in your subscription, using names based on your function app name:
- A resource group, which is a logical container for related resources.
- A standard Azure Storage account, which maintains state and other information about your projects.
- A consumption plan, which defines the underlying host for your serverless function app.
- A function app, which provides the environment for executing your function code. A function app lets you group functions as a logical unit for easier management, deployment, and sharing of resources within the same hosting plan.
- An Application Insights instance connected to the function app, which tracks usage of your serverless function.
Deploy the code
- In the WORKSPACE section of the Azure bar select the Deploy… button, and then select Deploy to Function App….
- When prompted to Select a resource, choose the function app you created in the previous section.
- Confirm that you want to deploy your function by selecting Deploy on the confirmation prompt. ImportantPublishing to an existing function overwrites any previous deployments.
Run the function in Azure
- Back in the Resources area in the side bar, expand your subscription, your new function app, and Functions. Right-click the
HttpExamplefunction and choose Execute Function Now….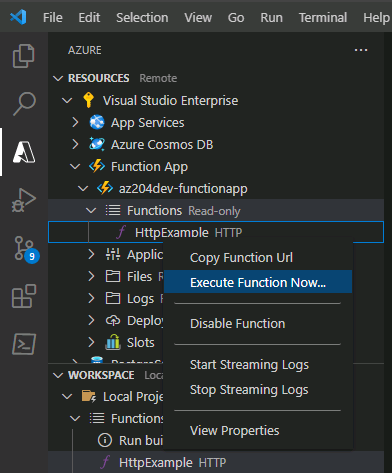
- In Enter request body you see the request message body value of
{ "name": "Azure" }. Press Enter to send this request message to your function. - When the function executes in Azure and returns a response, a notification is raised in Visual Studio Code.

