- Python and REST APIs: Interacting With Web Services – Real Python
- Requests: HTTP for Humans™ — Requests 2.27.1 documentation (python-requests.org)
- ติดตั้ง requests
- ทดลองเรียกแบบ GET
- ทดลองเรียกแบบ GET ที่เป็น trust a self signed SSL certificate
- ทดลองเรียกแบบ POST
ทดลองเรียกแบบ POST
1. ติดตั้ง requests
python -m pip install requests
2. ทดลองเรียกแบบ GET
import requests api_url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1" response = requests.get(api_url) print(response.status_code) print(response.headers["Content-Type"]) print(response.json())
200
application/json; charset=utf-8
{'userId': 1, 'id': 1, 'title': 'delectus aut autem', 'completed': False}
3. ทดลองเรียกแบบ GET ที่เป็น trust a self signed SSL certificate
เช่น สร้างโปรเจ็กส์ webapi ขึ้นมาด้วย .Net 6 แล้วรันแบบ localhost ก็จะเป็นแบบ self signed SSL certificate
import requests api_url = "https://localhost:7237/WeatherForecast" response = requests.get(api_url) print(response.status_code) print(response.headers["Content-Type"]) print(response.json())
จะได้ error
requests.exceptions.SSLError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='localhost', port=7237): Max retries exceeded with url: /WeatherForecast (Caused by SSLError(SSLCertVerificationError(1, '[SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed: self signed certificate (_ssl.c:1129)')))
วิธีแก้
ให้ทำการ export certificate ไฟล์ ออกมาจาก chrome ก่อน โดยไปที่ More tools | Developer tools
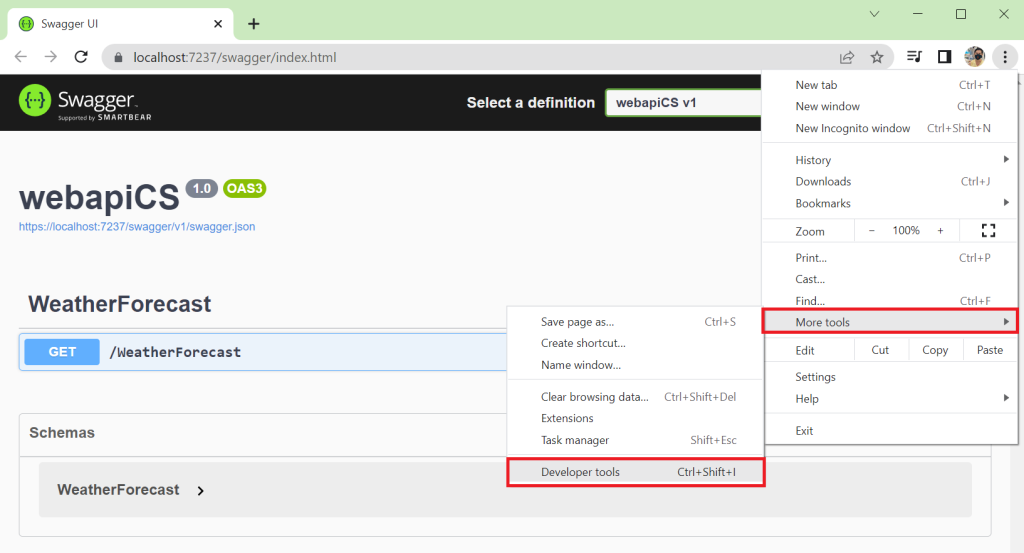
ไปที่ Security | Overview แล้วคลิกที่ View certificate
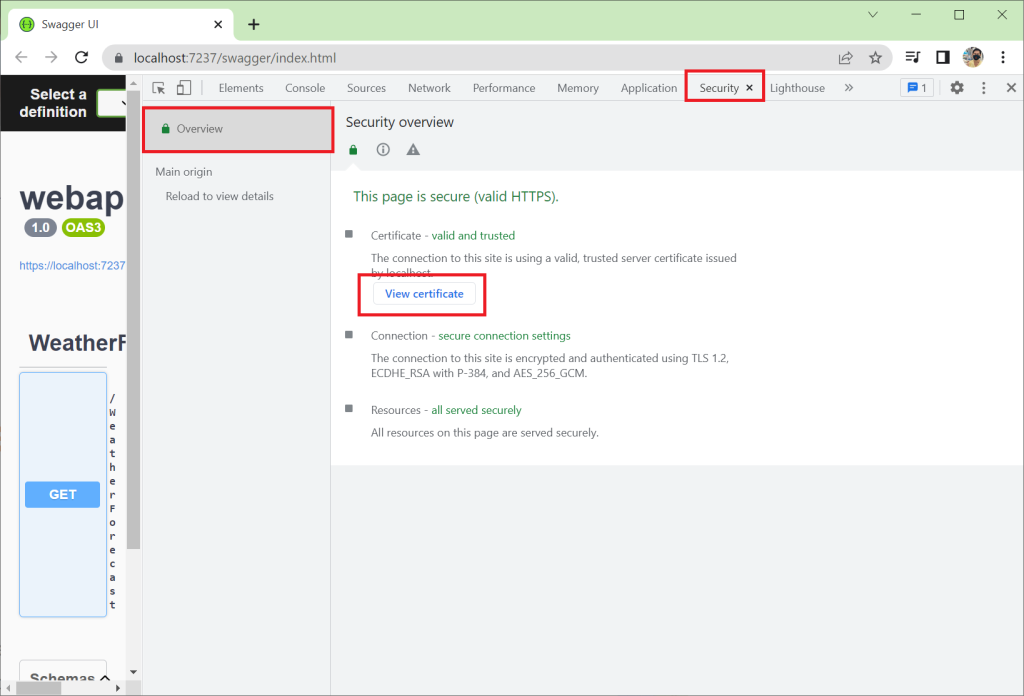
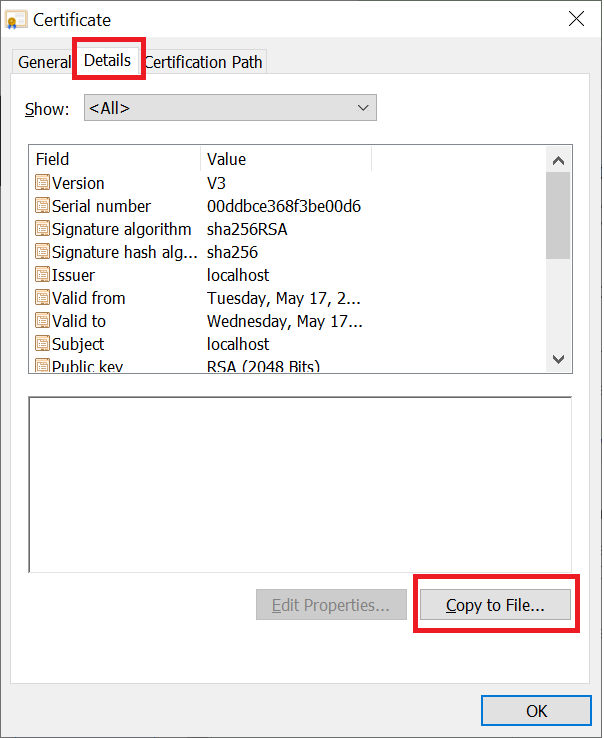
ที่แท็ป Details เลือก Copy to File…
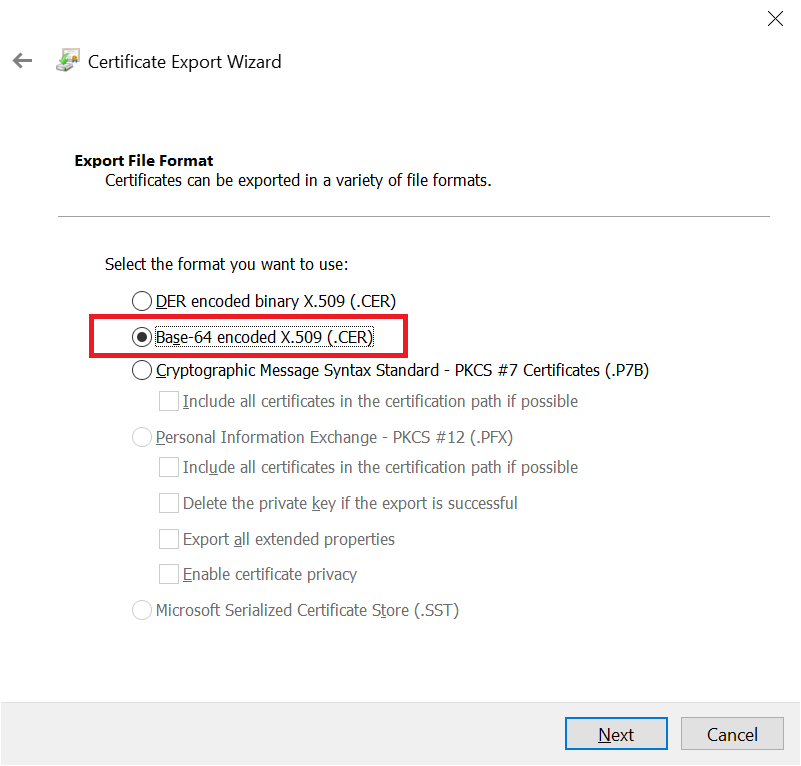
แล้วเลือก Base64 encoded X.509 (.CER)
ปรับโคีด Python ให้อ้างถึงไฟล์ .cer
- use python requests module to access asp.net core localhost pages with self signed https certificate – Stack Overflow
- How to get Python requests to trust a self signed SSL certificate? – Stack Overflow
import requests api_url = "https://localhost:7237/WeatherForecast" response = requests.get(api_url, verify='./webapiCS.cer') print(response.status_code) print(response.headers["Content-Type"]) print(response.json())
200
application/json; charset=utf-8
[{'date': '2022-05-18T15:16:09.823195+07:00', 'temperatureC': -3, 'temperatureF': 27, 'summary': 'Mild'}, {'date': '2022-05-19T15:16:09.823412+07:00', 'temperatureC': -7, 'temperatureF': 20, 'summary': 'Cool'}, {'date': '2022-05-20T15:16:09.823414+07:00', 'temperatureC': -17, 'temperatureF': 2, 'summary': 'Warm'}, {'date': '2022-05-21T15:16:09.8234141+07:00', 'temperatureC': 7, 'temperatureF': 44, 'summary': 'Warm'}, {'date': '2022-05-22T15:16:09.8234142+07:00', 'temperatureC': -4, 'temperatureF': 25, 'summary': 'Hot'}]
หรือแก้ไขด้วยการไม่ต้อง verify
r = requests.get(url, verify=False)
4. ทดลองเรียกแบบ POST
import requests
api_url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos"
todo = {"userId": 1, "title": "Buy milk", "completed": False}
response = requests.post(api_url, json=todo)
response.json()
print(response.status_code)
print(response.headers["Content-Type"])
print(response.json())
201
application/json; charset=utf-8
{'userId': 1, 'title': 'Buy milk', 'completed': False, 'id': 201}
หรือ
import requests
import json
api_url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos"
todo = {"userId": 1, "title": "Buy milk", "completed": False}
headers = {"Content-Type":"application/json"}
response = requests.post(api_url, data=json.dumps(todo), headers=headers)
response.json()
print(response.status_code)
print(response.headers["Content-Type"])
print(response.json())
