- To install Apache Spark and run Pyspark in Ubuntu 22.04 – DEV Community
- Install Apache Spark on Ubuntu 22.04|20.04|18.04 | ComputingForGeeks
ติดตั้ง java
update packages
$ sudo apt update
ติดตั้ง Java JDK (openjdk)
$ sudo apt install default-jdk
ตรวจสอบการติดตั้งบน Ubuntu 22.04.2
$ java --version openjdk 11.0.19 2023-04-18 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.19+7-post-Ubuntu-0ubuntu122.04.1) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.19+7-post-Ubuntu-0ubuntu122.04.1, mixed mode, sharing)
ติดตั้ง Apache Spark
ติดตั้ง package curl , mlocate , git , scala
$ sudo apt install curl mlocate git scala
ดาว์นโหลด Apache Spark จาก Download Apache Spark™
$ wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/spark/spark-3.3.2/spark-3.3.2-bin-hadoop3.tgz
แตกไฟล์
$ tar xvf spark-3.3.2-bin-hadoop3.tgz
ย้ายไฟล์
$ sudo mv spark-3.3.2-bin-hadoop3/ /opt/spark
Set Spark environment
$ sudo nano ~/.bashrc
ใส่ค่านี้ต่อที่ด้านล่างของไฟล์ .bashrc
export SPARK_HOME=/opt/spark
export PATH=$PATH:$SPARK_HOME/bin:$SPARK_HOME/sbin
export SPARK_LOCAL_IP=localhost
export PYSPARK_PYTHON=/usr/bin/python3
export PYTHONPATH=$(ZIPS=("$SPARK_HOME"/python/lib/*.zip); IFS=:; echo "${ZIPS[*]}"):$PYTHONPATH
$ source .bashrc
run Spark shell
$ spark-shell
run Pyspark
$ pyspark
Python 3.10.6 (main, Nov 14 2022, 16:10:14) [GCC 11.3.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
Setting default log level to "WARN".
To adjust logging level use sc.setLogLevel(newLevel). For SparkR, use setLogLevel(newLevel).
23/07/28 23:41:19 WARN NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/__ / .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version 3.3.2
/_/
Using Python version 3.10.6 (main, Nov 14 2022 16:10:14)
Spark context Web UI available at http://localhost:4040
Spark context available as 'sc' (master = local[*], app id = local-1690562479751).
SparkSession available as 'spark'.
>>>
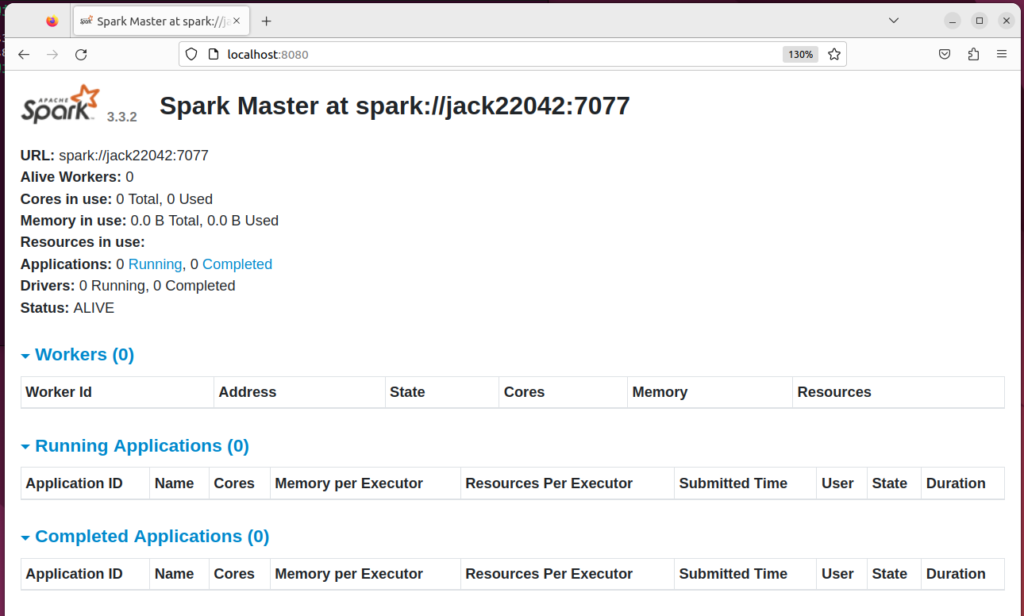
Start a standalone master server
$ start-master.sh starting org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master, logging to /opt/spark/logs/spark-jack-org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master-1-jack22042.out
The process will be listening on TCP port 8080.
$ sudo ss -tunelp | grep 8080
tcp LISTEN 0 1 [::ffff:127.0.0.1]:8080 *:* users:(("java",pid=6346,fd=283)) uid:1000 ino:63398 sk:e cgroup:/user.slice/user-1000.slice/session-4.scope v6only:0 <->
The Web UI looks like below. http://localhost:8080
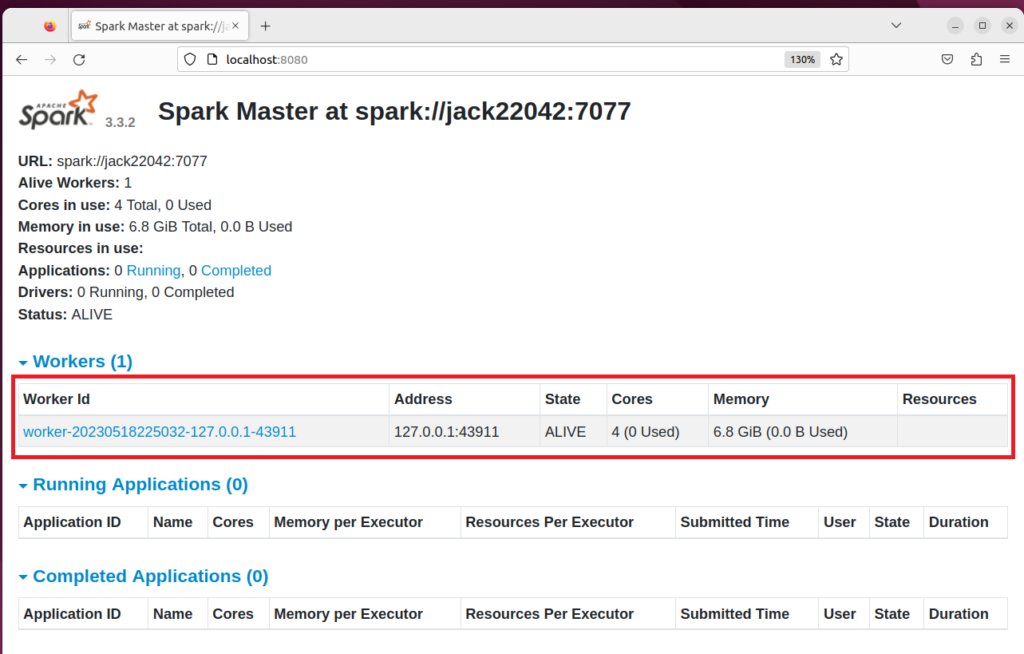
Starting Spark Worker Process
$ start-worker.sh spark://jack22042:7077 starting org.apache.spark.deploy.worker.Worker, logging to /opt/spark/logs/spark-jack-org.apache.spark.deploy.worker.Worker-1-jack22042.out
shut down the master and slave Spark processes
$ stop-worker.sh $ stop-master.sh
